자잘한 기술부채
✅Batch Insert
batch insert란, 여러 개의 SQL Statement를 하나의 구문으로 처리하는 것을 의미한다.
-
본래라면 한 SQL 구문 당 하나의 트랜잭션이 할당되지만, Batch Insert으로 처리하면 여러 SQL Statement가 하나의 트랜잭션으로 묶이게 된다.
-
대량의 데이터를 Insert/Delete해야 하는 상황에서 쿼리 처리 성능을 향상시킬 수 있다.
-
설정 방법
spring: jpa: database: mysql properties: hibernate.jdbc.batch_size: 50 hibernate.order_inserts: true hibernate.order_updates: true hibernate.dialect: org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect hibernate.show_sql: truehibernate.jdbc.batch_size: Batch Insert의 Size를 지정한다. 이 값에 따라 한번에 Insert되는 Row의 개수가 결정된다.hibernate.order_updates, hibernate.order_inserts: 같은 구문끼리 정렬을 한 뒤 구문을 실행하도록 하는 옵션이다.
-
동작 원리
- java의 addBatch는 하나의 SQL 구문이 등록되면 그 복사본을 만든다.
- 이후 작성되는 구문들은 해당 복사본 구문을 커밋될 때까지 재사용한다.
-
Entity Key 생성 전략을 IDENTITY로 하면 batch 옵션이 동작하지 않는다.
- 쿼리가 수행된 후에 값을 얻을 수 있기 때문에, 한꺼번에 값을 보내는 batch insert가 불가하다.
- 때문에 Spring Data JDBC를 사용하거나, Spring Data JPA에서 Entity Key 생성 전략을 SEQUENCE로 사용하는 것이 권장된다.
spring data jpa batch insert 정리
✅@EventListener
- EventListener을 사용하기 전
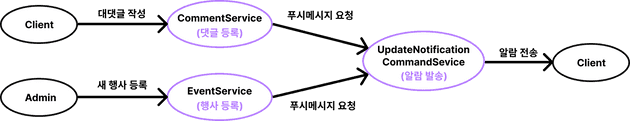 유저가 대댓글을 작성하면 댓글 작성자에게 알람이 간다. 관리자가 행사를 새로 등록하면, 해당 행사의 태그를 관심등록한 사용자에게 알람이 간다.
이 동작을 UpdateNotificationCommandService에서 처리한다.
유저가 대댓글을 작성하면 댓글 작성자에게 알람이 간다. 관리자가 행사를 새로 등록하면, 해당 행사의 태그를 관심등록한 사용자에게 알람이 간다.
이 동작을 UpdateNotificationCommandService에서 처리한다. - EventListener를 사용한 후
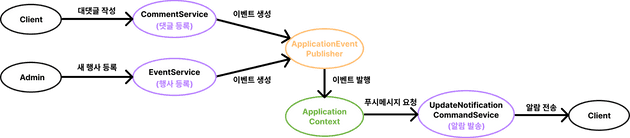
Event를 사용하는 주된 이유는 서비스 간의 의존성을 줄이기 위함이다.
Spring Event는 크게 Event Clsss와 이벤트를 발행하는 Event Publisher, 이벤트를 받아들이는 Event Listener 3가지 요소로 구성된다.
-
Event Class : 이벤트를 처리하는 데 필요한 데이터를 가지고 있다.
예시 이미지에는 없지만 CommentService, EventService가 생성하는 UpdateNotificationEvent라는 도메인 객체가 이에 해당한다.
@Getter public class UpdateNotificationEvent { private final Long receiverId; private final Long redirectId; private final String updateNotificationType; private final LocalDateTime createdAt; public UpdateNotificationEvent( final Long receiverId, final Long redirectId, final String updateNotificationType ) { this.receiverId = receiverId; this.redirectId = redirectId; this.updateNotificationType = updateNotificationType; this.createdAt = LocalDateTime.now(); } } -
Event Publisher : ApplicationEventPublisher 빈을 주입하고 publishEvent() 메서드를 통해 생성된 이벤트 객체를 넣어주면 된다.
예시에서 CommentService, EventService가 이에 해당한다.
@Slf4j @Service public class CommentService { ApplicationEventPublisher publisher; ... public void create(/* 생략 */) { ... publisher.publishEvent(new UpdateNotificationEvent(/* ... */)); } } -
Event Listener : 발생한 이벤트를 캐치해서 @EventListener 어노테이션으로 정의한 메서드를 호출할 수 있다.
예시에서는 UpdateNotificationCommandService가 이에 해당한다.
@Service @RequiredArgsConstructor public class UpdateNotificationCommandService { private final UpdateNotificationRepository updateNotificationRepository; private final FirebaseCloudMessageClient firebaseCloudMessageClient; @EventListener public void createUpdateNotification(final UpdateNotificationEvent updateNotificationEvent) { /** 사용자에게 푸시 알람 보내는 코드 **/ } }
스프링 이벤트는 기본적으로 동기 방식으로 동작하기 때문에, 비동기로 처리하게 하면 성능을 높일 수 있다.
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class EmmSaleApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EmmSaleApplication.class, args);
}
}@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class UpdateNotificationCommandService {
private final UpdateNotificationRepository updateNotificationRepository;
private final FirebaseCloudMessageClient firebaseCloudMessageClient;
@Async
@EventListener
public void createUpdateNotification(final UpdateNotificationEvent updateNotificationEvent) {
/** 사용자에게 푸시 알람 보내는 코드 **/
}
}@EnableAsync 어노테이션을 통해 비동기를 사용하겠다고 선언하고, 비동기로 동작하고자 하는 메서드에 @Async 어노테이션을 설정해주면 된다.
